[TOC]
可能显示有点问题,可查看pdf:https://github.com/Narcissuscyn/Algorithm/blob/master/from_encoder_decoder_to_transformer.pdf
Encoder-Decoder
在Quara上有一个问题:https://www.quora.com/What-is-an-Encoder-Decoder-in-Deep-Learning,其中Rohan Saxena的回答我觉得挺好理解的,从横向和纵向两个方向来解释这个问题。
横向分析
首先说了特征表示在机器学习里面的重要性,从早期的手工特征(如HOG)到现在使用神经网络进行特征学习(The first few layers of a neural network extract features from the data, or in other words map raw inputs to efficient feature representations. The next few layers (typically fully connected layers) mix and match and combine these features to produce an output.),都是为了得到好的特征表达。
而一些网络结构被设计用来提取有效的特征表达:
They use an encoder network to map raw inputs to feature representations, and a decoder network to take this feature representation as input, process it to make its decision, and produce an output. This is called an encoder-decoder network.
encoder和decoder是可以分开使用的,但是常常被结合使用以取得好的效果。
纵向分析
CNN Encoder-Decoder
In a CNN, an encoder-decoder network typically looks like this (a CNN encoder and a CNN decoder):
This is a network to perform semantic segmentation of an image. The left half of the network maps raw image pixels to a rich representation of a collection of feature vectors. The right half of the network takes these features, produces an output and maps the output back into the “raw” format (in this case, image pixels).
RNN Encoder-Decoder
In an RNN, an encoder-decoder network typically looks like this (an RNN encoder and an RNN decoder):
This is a network to predict responses for incoming emails. The left half of the network encodes the email into a feature vector, and the right half of the network decodes the feature vector to produce word predictions.
**Mixed Style Encoder-Decoder **
Note that it is not necessary to use just CNN or just RNN for encoder and decoder. We can mix and match and use a CNN encoder with RNN decoder, or vice versa; any combination can be used which is suitable for the given task.
An example from a paper I recently implemented from scratch, Text-guided Attention Model for Image Captioning (T-ATT):
Look at the parts I have highlighted in red. The STV refers to Skip-Thought Vectors. STV in itself is an encoder-decoder architecture.
Sequence-to-Sequence
Sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq)* 模型,顾名思义,其输入是一个序列,输出也是一个序列,例如输入是英文句子,输出则是翻译的中文。2014 Google提出Sequence-to-sequence的概念(待考证),在这之前也有使用encoder-decoder来解决sequence2sequence任务的,比如Bengio在2014年的论文中提出,提供了一种崭新的RNN Encoder-Decoder算法,并且将其应用于机器翻译中。seq2seq 可以用在很多方面:机器翻译、QA 系统、文档摘要生成、Image Captioning (图片描述生成器)。
Example
对于下面这个简单的示例模型,分为encoder-encoder vector-encoder三个部分。

Encoder和Decoder都是一个由RNN堆叠而成的网络,其实Sequence2Sequence的结构主要是使用的encoder-to-decoder的架构。我觉得seq2seq和auto-encoder是encoder-decoder衍生出来的、针对不同任务的框架,Seq2Seq的主要特点就是输入和输出长度可以不一样,而auto-encoder就是为了对输入进行重建。
Attention
上面所提及的Encoder-Decoder模型是有弊端的:
- 随着输入信息长度的增加,由于向量长度固定,先前编码好的信息会被后来的信息覆盖,丢失很多信息(当使用RNN作为Encoder时,由于其长短期记忆能力的有限,当输入信息长度变大,信息丢失严重)。中间语义向量无法完全表达整个输入序列的信息。(this fixed-length context vector design is incapability of remembering long sentences.)//(2015年的文章Bahdanau et al., 2015就是针对这个问题的。The attention mechanism was born to help **memorize long source sentences** in neural machine translation(Bahdanau et al., 2015))。
- 而且,每个输入的贡献都是一样的。
因此,在很多方面都出现了改进的模型,包括以下方面:s
I consider the approach of reversing a sentence a “hack”. It makes things work better in practice, but it’s not a principled solution. Most translation benchmarks are done on languages like French and German, which are quite similar to English (even Chinese word order is quite similar to English). But there are languages (like Japanese) where the last word of a sentence could be highly predictive of the first word in an English translation. In that case, reversing the input would make things worse. So, what’s an alternative? Attention Mechanisms.//某些时候是不可行的
-
Using LSTM or GRU cells.
而Attention就是一种通用的方法,在这部分呢,就来学习一下Attention 的思想.
神经网络中的注意机制基于人类中发现的视觉注意机制:
Attention Mechanisms in Neural Networks are (very) loosely based on the visual attention mechanism found in humans. Human visual attention is well-studied and while there exist different models, all of them essentially come down to being able to focus on a certain region of an image with “high resolution” while perceiving the surrounding image in “low resolution”, and then adjusting the focal point over time.
在早期就有使用这种attention的思想,但是最近几年才在深度学习领域火起来,下面举一个机器翻译里面应用attention的例子。
Attention In Bahdanau et al., 2015
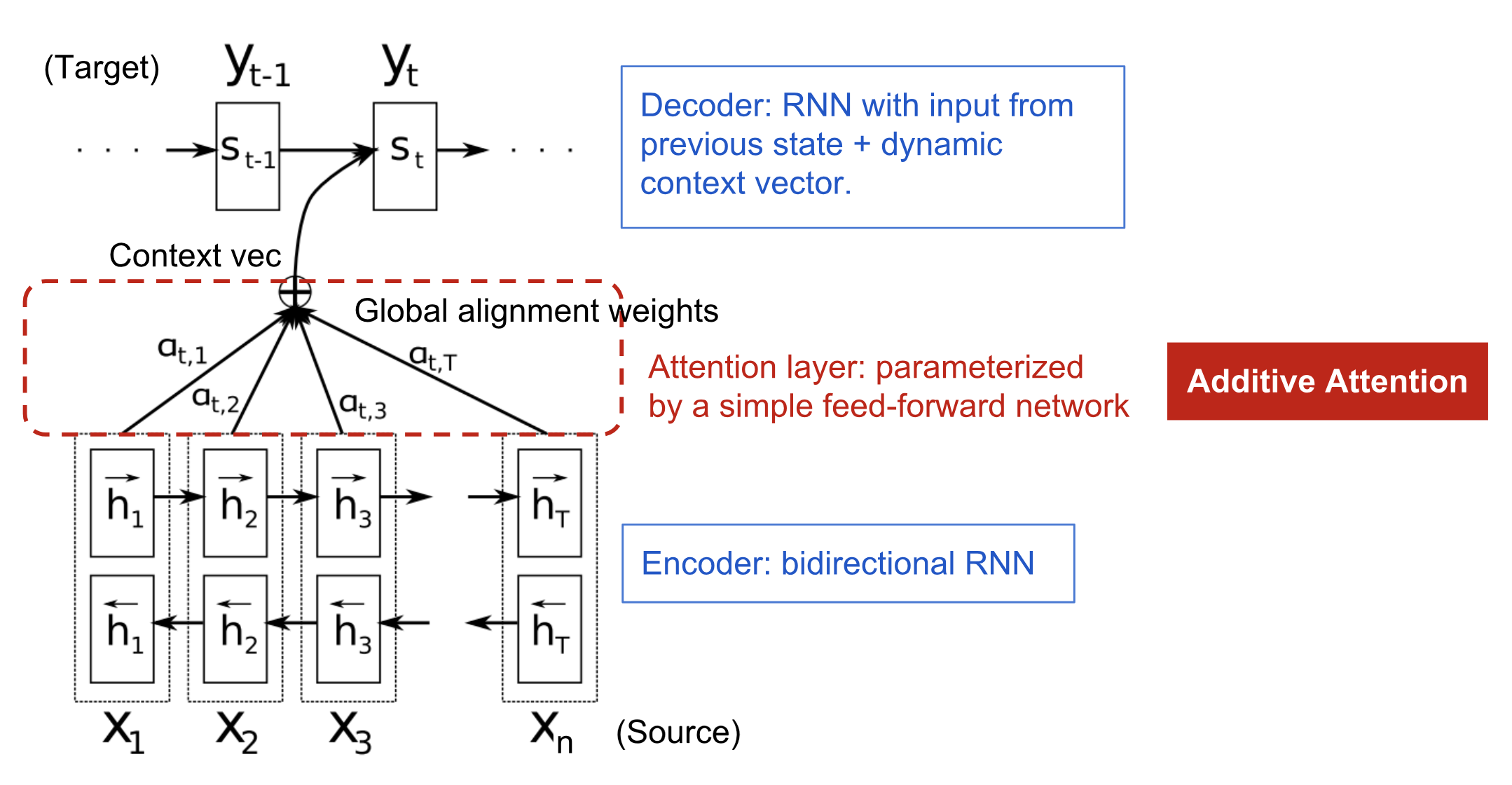
X为输入序列,y为预测序列,我们可以看到这个双向RNN的所有隐藏层输出被一个权重向量$\alpha$加权结合起来了,不再像以前一样,只使用最后一个隐藏层的输出:
The
are typically normalized to sum to 1 (so they are a distribution over the input states)
这个$\alpha$是一个矩阵,第t行($t=1……n$)表示$h_1,……,h_n$对$y_t$的输出所作的贡献,也就是说在decoder中,$y_{t-1}$和$\sum_{i=1}^n \alpha_{t,i} \boldsymbol{h}_i $作为t时刻Decoder的输入。
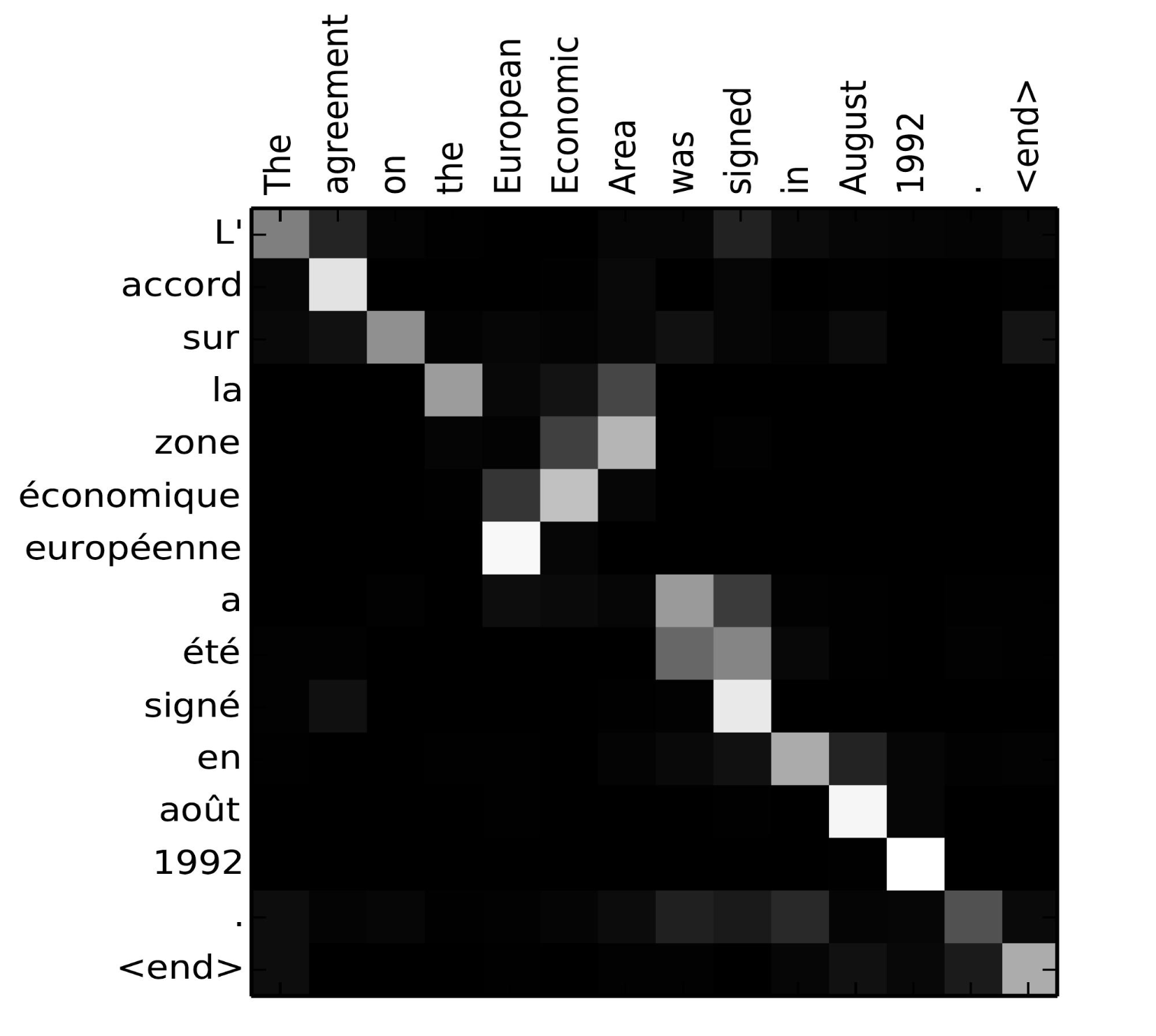
在这篇文章中,$\alpha$如何得到呢?通过一个单层隐藏层学得,$t$时刻$h_i$对$s_t$ or $y_t$的作用分数为: $V^T_a$和$W_a$都是待学习参数。以下就是学得的作用关系图,越亮,表示输入$x_i$对输出$y_j$的作用越大:
Attention or Memory
引入attention往往会引入新的计算代价,比如说处理上百的token sequence时,每个timestep输出的是h-dim的,那就会增加很多计算量:
Actually, that’s quite counterintuitive. Human attention is something that’s supposed to savecomputational resources. By focusing on one thing, we can neglect many other things. But that’s not really what we’re doing in the above model. We’re essentially looking at everything in detail before deciding what to focus on. Intuitively that’s equivalent outputting a translated word, and then going back through all of your internal memory of the text in order to decide which word to produce next. That seems like a waste, and not at all what humans are doing. In fact, it’s more akin to memory access,In this interpretation, instead of choosing what to “attend” to, the network chooses what to retrieve from memory. not attention, which in my opinion is somewhat of a misnomer (more on that below). Still, that hasn’t stopped attention mechanisms from becoming quite popular and performing well on many tasks.
An alternative approach to attention is to use Reinforcement Learning to predict an approximate location to focus to. That sounds a lot more like human attention, and that’s what’s done in Recurrent Models of Visual Attention.
Memory Mechanisms themselves have a much longer history……
Attention Family
With the help of the attention, the dependencies between source and target sequences are not restricted by the in-between distance anymore! Given the big improvement by attention in machine translation, it soon got extended into the computer vision field (Xu et al. 2015) and people started exploring various other forms of attention mechanisms (Luong, et al., 2015; Britz et al., 2017; Vaswani, et al., 2017).
| Name | Alignment score function | Citation |
|---|---|---|
| Content-base attention | $\text{score}(\boldsymbol{s}_t, \boldsymbol{h}_i) = \text{cosine}[\boldsymbol{s}_t, \boldsymbol{h}_i]$ | Graves2014 |
| Additive(*) | $\text{score}(\boldsymbol{s}_t, \boldsymbol{h}_i) = \mathbf{v}_a^\top \tanh(\mathbf{W}_a[\boldsymbol{s}_t; \boldsymbol{h}_i])$ | Bahdanau2015 |
| Location-Base | $\alpha_{t,i} = \text{softmax}(\mathbf{W}_a \boldsymbol{s}_t)$ Note: This simplifies the softmax alignment to only depend on the target position. |
Luong2015 |
| General | $\text{score}(\boldsymbol{s}_t, \boldsymbol{h}_i) = \boldsymbol{s}_t^\top\mathbf{W}_a\boldsymbol{h}_i$ where $W_a$ is a trainable weight matrix in the attention layer. |
Luong2015 |
| Dot-Product | $\text{score}(\boldsymbol{s}_t, \boldsymbol{h}_i) = \boldsymbol{s}_t^\top\boldsymbol{h}_i$ | Luong2015 |
| Scaled Dot-Product(^) | $\text{score}(\boldsymbol{s}_t, \boldsymbol{h}_i) = \frac{\boldsymbol{s}_t^\top\boldsymbol{h}_i}{\sqrt{n}}$ Note: very similar to the dot-product attention except for a scaling factor; where n is the dimension of the source hidden state. |
(*) Referred to as “concat” in Luong, et al., 2015 and as “additive attention” in Vaswani, et al., 2017. (^) It adds a scaling factor $1/\sqrt{n}$, motivated by the concern when the input is large, the softmax function may have an extremely small gradient, hard for efficient learning.
Attention分类
| Name | Definition | Citation |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Attention(&) | Relating different positions of the same input sequence. Theoretically the self-attention can adopt any score functions above, but just replace the target sequence with the same input sequence. | Cheng2016 |
| Global/Soft | Attending to the entire input state space. | Xu2015 |
| Local/Hard | Attending to the part of input state space; i.e. a patch of the input image. | Xu2015; Luong2015 |
(&) Also, referred to as “intra-attention” in Cheng et al., 2016 and some other papers.
接下来具体讲一些详细的Attention
Self-Attention
也叫intra-attention,在机器阅读、文章摘要、图像描述生成等领域很有用,也就是在同一个句子里面进行不同位置的attention,以在句子内部产生一个关联性信息的表达。
Soft vs Hard Attention
在 show, attend and tell 这篇文章中,提出soft\hard两种attention,不同在于两种attention所获取的信息不同,soft attention关注整张图像,而hard attention则关注图像部分区域,两者各有优势和劣势:
- soft:
- 优点:模型平滑、可微
- 缺点:当输入较大时,计算量大;
- hard
- 优势:在测试阶段计算量小
- 劣势:不可微,需要借助variance reduction 或 reinforcement learning来训练
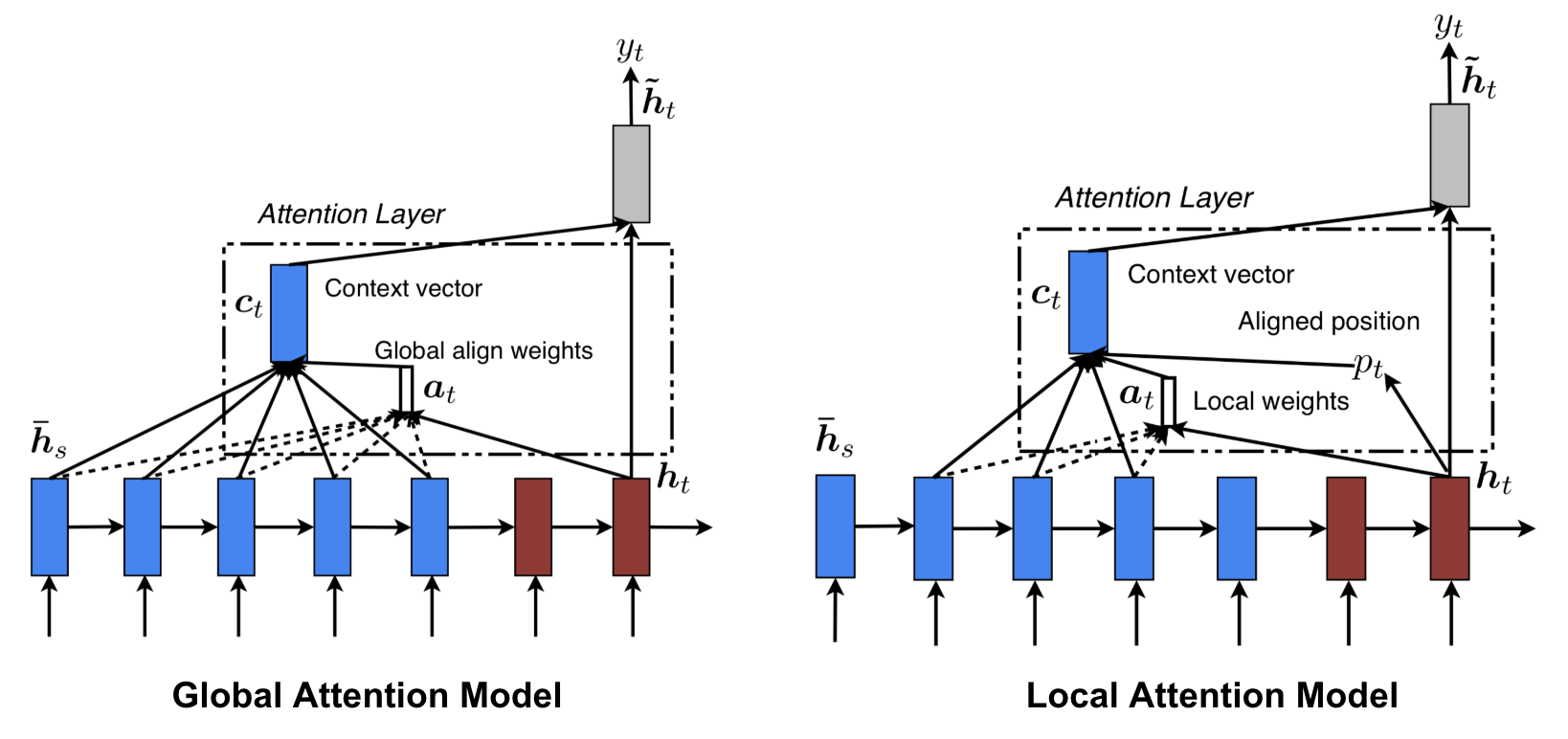
Global vs. Local Attention
Luong, et al., 2015提出了两种attention,global attention类似于soft attention,而local attention是hard attentiond和soft attention的协调,它是可微的:
the model first predicts a single aligned position for the current target word and a window centered around the source position is then used to compute a context vector.
NMT
在介绍Transformer之前,我们介绍下NMT(Neural Turing Machines)。先来看下对Turing Machine的定义:
Alan Turing in 1936 proposed a minimalistic model of computation. It is composed of a infinitely long tape and a head to interact with the tape. The tape has countless cells on it, each filled with a symbol: 0, 1 or blank (“ “). The operation head can read symbols, edit symbols and move left/right on the tape. Theoretically a Turing machine can simulate any computer algorithm, irrespective of how complex or expensive the procedure might be. The infinite memory gives a Turing machine an edge to be mathematically limitless. However, infinite memory is not feasible in real modern computers and then we only consider Turing machine as a mathematical model of computation.
Fig. 9. How a Turing machine looks like: a tape + a head that handles the tape. (Image source: http://aturingmachine.com/)
再看下NTM的定义:
Neural Turing Machine (NTM, Graves, Wayne & Danihelka, 2014) is a model architecture for coupling a neural network with external memory storage. The memory mimics the Turing machine tape and the neural network controls the operation heads to read from or write to the tape. However, the memory in NTM is finite, and thus it probably looks more like a “Neural von Neumann Machine”.
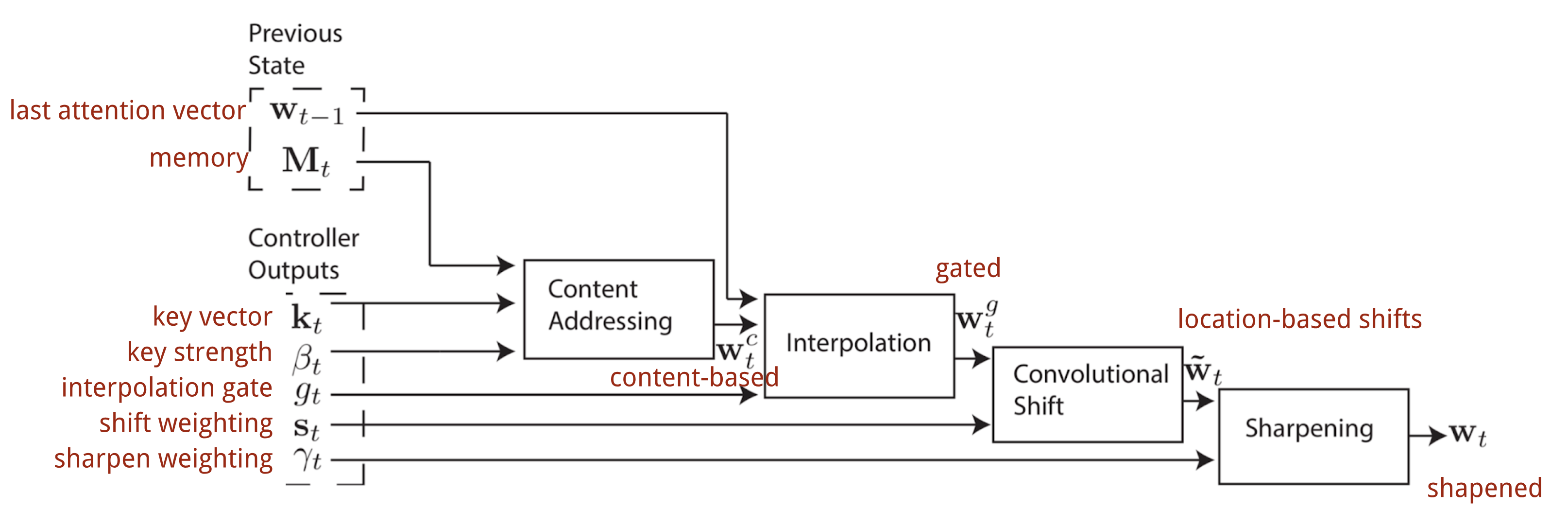
NTM包含一个Controller和一个memory bank。前者可以是任何形式的神经网络,后者则是$N×M$的存储矩阵。Controller在处理操作的时候并行的访问memory,所有的读取写入操作都是结合soft attention进行的,也就是说都读或写的数据加上权重。
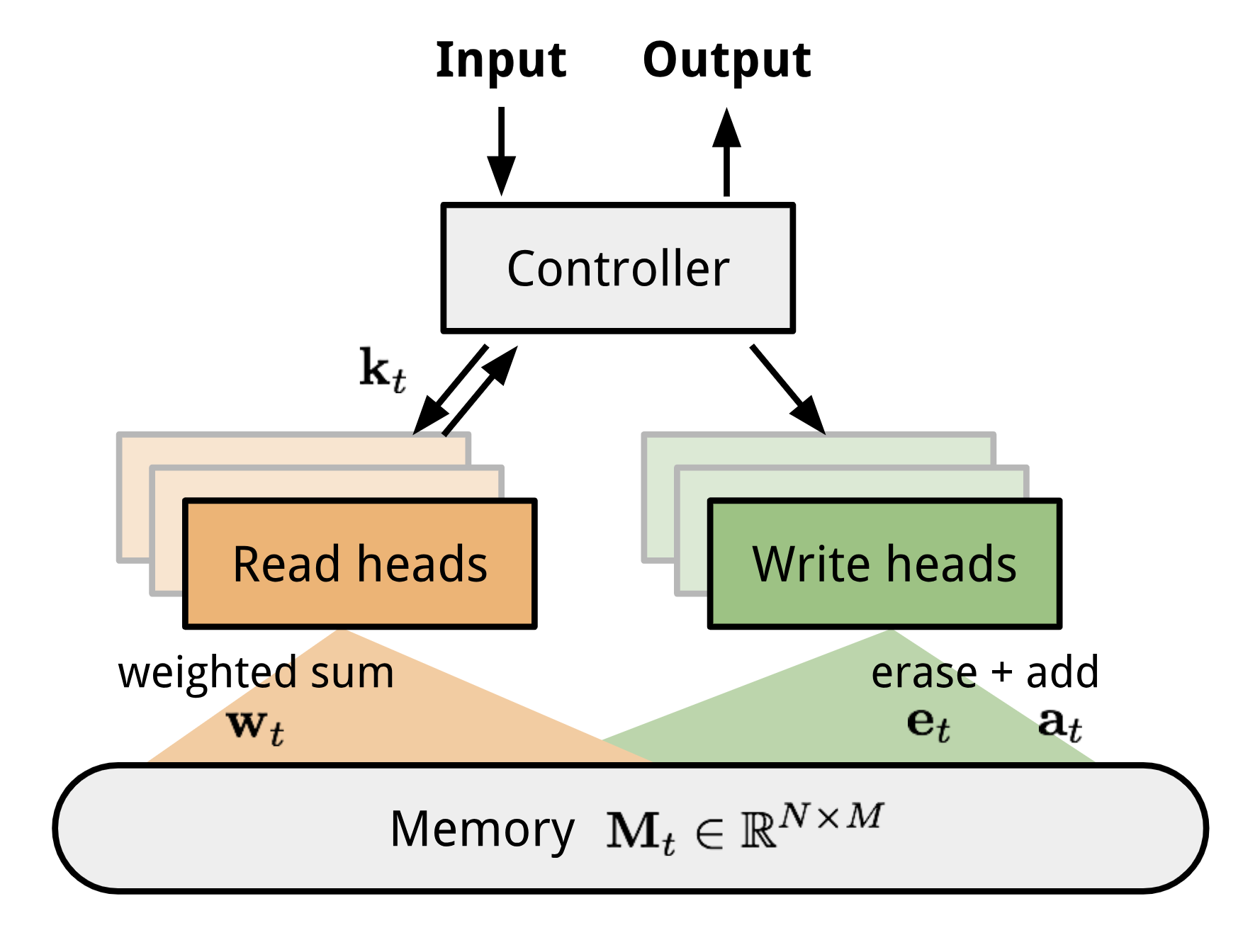
Fig 10. Neural Turing Machine Architecture.
读写操作
读取时,权重$w_t$控制对内存内容的行赋予权重: $w_t(i)$为第i个权重,$M_t(i)$为第i行内存向量。
写入时:
Attention机制
如何产生$w_t$呢?NTM使用了混合的 content-based 和location-based addressings。
Content-based addressing
Controller从input获得key vector $k_t$,计算它和memory row的cosine相似性,然后通过softmax进行归一化,另外引入$\beta_t$来放大或者缩小分布的关注重点:
Interpolation
计算了上步中的attention之后,我们结合上个timestep所产生的的 content-based attention计算最终的 content-based attention:
Location-based addressing
location-based addressing就是将attention vector中不同位置的值加权起来,具体就是通过允许整数移位的加权分布(a weighting distribution over allowable integer shifts)进行加权,它等价于卷积核(关于位置的偏移)为$s_t(·)$的一维卷积,有很多方式来定义这个分布:
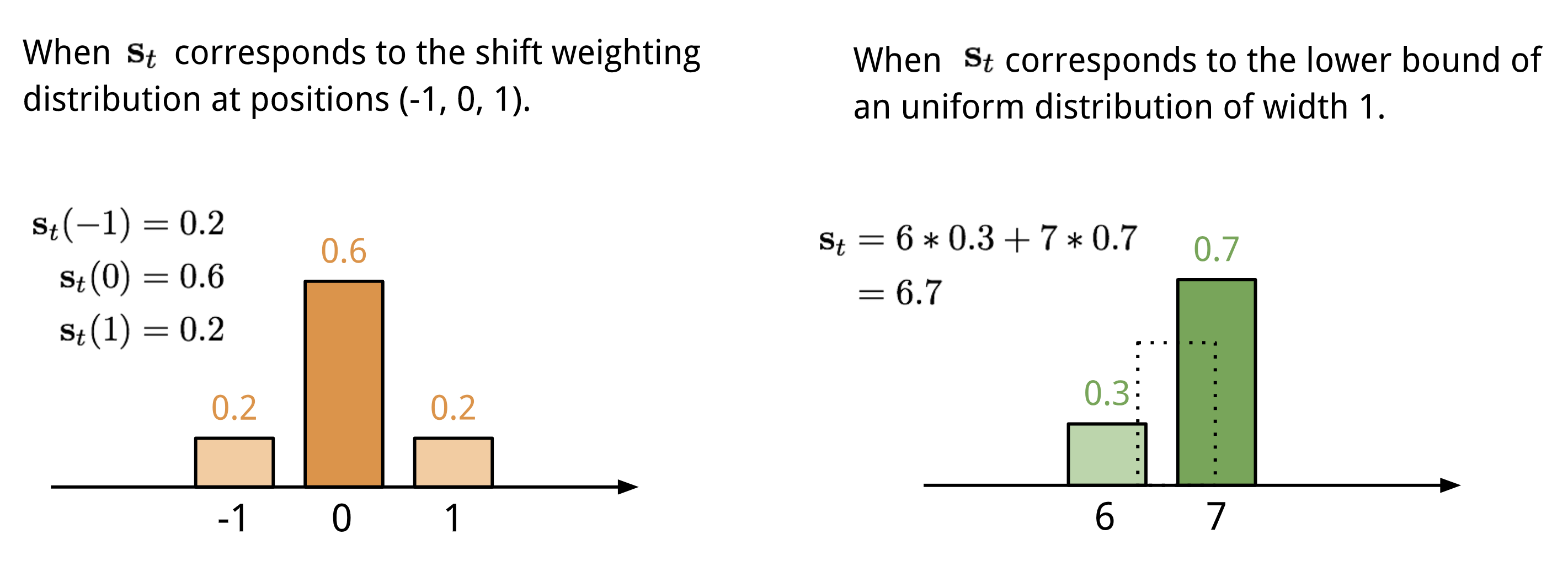
最终的attention经过$\gamma_t\ge1$来加强锐化: 整个产生$w_t$的过程如下所示,如果有并行的read和write操作,则controller将产生多组输出:
Transformer
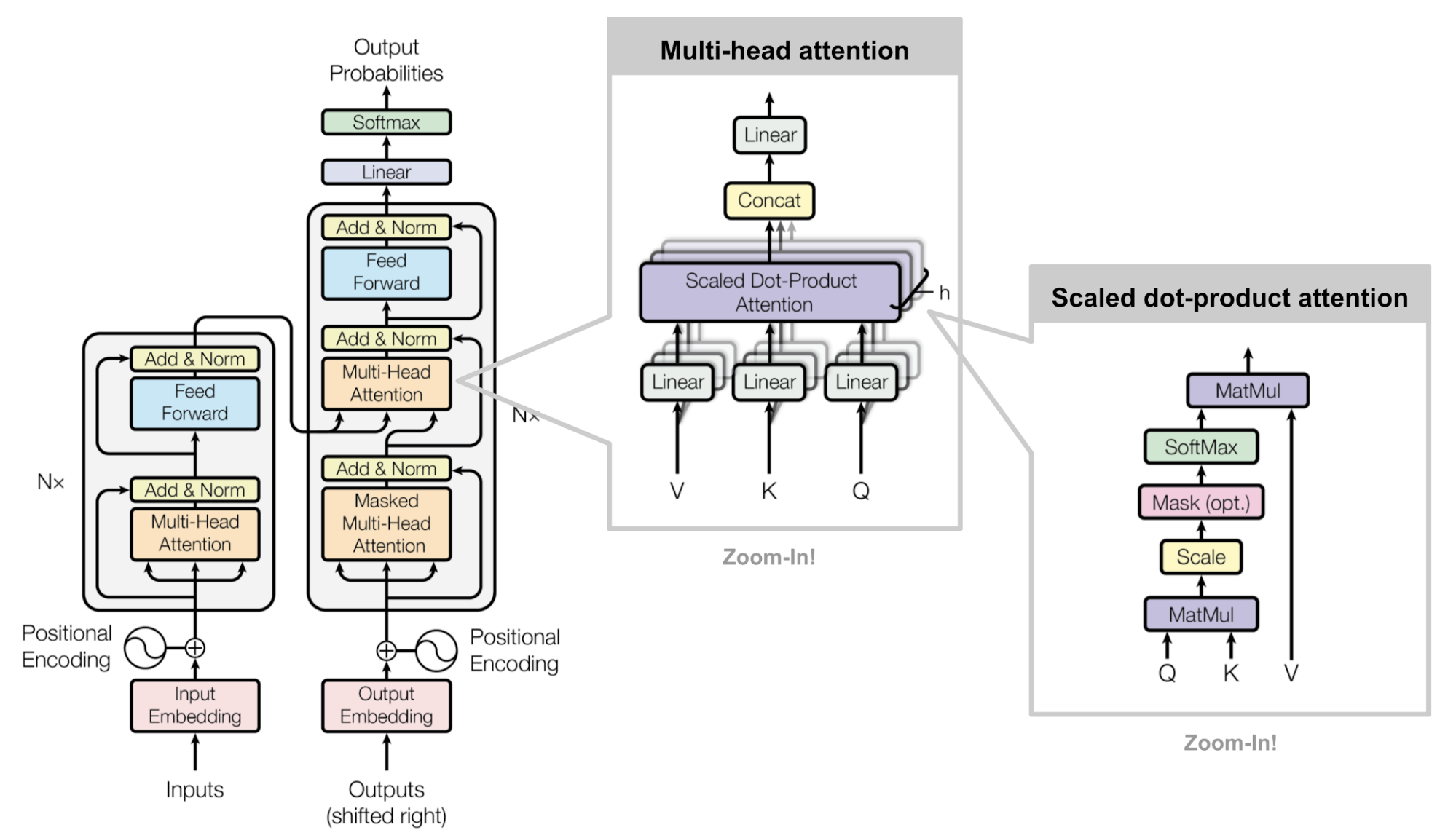
Transformer是“Attention is All you Need” (Vaswani, et al., 2017)提出的一中soft attention,它使得不使用RNN units进行seq2seq的任务解决成为可能,Transformer模型完全建立在self-attention机制之上,并使用sequence-aligned recurrent architecture。这个模型最初是为了提高机器翻译的效率,因为RNN是顺序执行的,t时刻没有完成就不能处理t+1时刻,因此很难并行,但Transformer的Self-Attention机制和Position Encoding可以替代RNN,从而实现效率。后来发现Self-Attention效果很好,在很多其它的地方也可以使用Transformer模型。这包括著名的OpenAI GPT和BERT模型,都是以Transformer为基础的。当然它们只使用了Transformer的Decoder部分,由于没有了Encoder,Decoder只有Self-Attention而没有普通的Attention。
Key, Value and Query
主要组件是multi-head self-attention mechanism部分,它将输入和其编码表达看成key-value(K-V)对,且维度都是序列长度$n$。根据神经机器翻译的思想,(K,V)就是encoder 的隐藏状态;上一个输出被压缩成一个query(Q, m-dim),那么下一个输出,其实就是对(K,V,Q)的一个映射。
这里使用的attention是 前面表中scaled dot-product attention,针对V进行加权:
Multi-Head Self-Attention
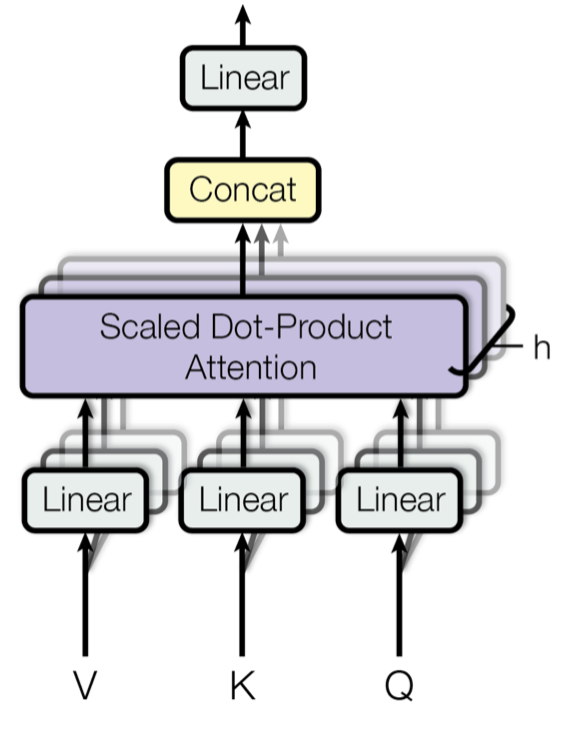
主要思想就是并行的运行这个scaled dot-product attention多次,然后拼接之后通过线性变换获取最终的attention,根据论文描述:
“multi-head attention allows the model to jointly attend to information from different representation subspaces at different positions. With a single attention head, averaging inhibits this.”
公式为: $W_i^Q,W_i^K,W_i^V,W^O$都是需要学习的参数。
Encoder
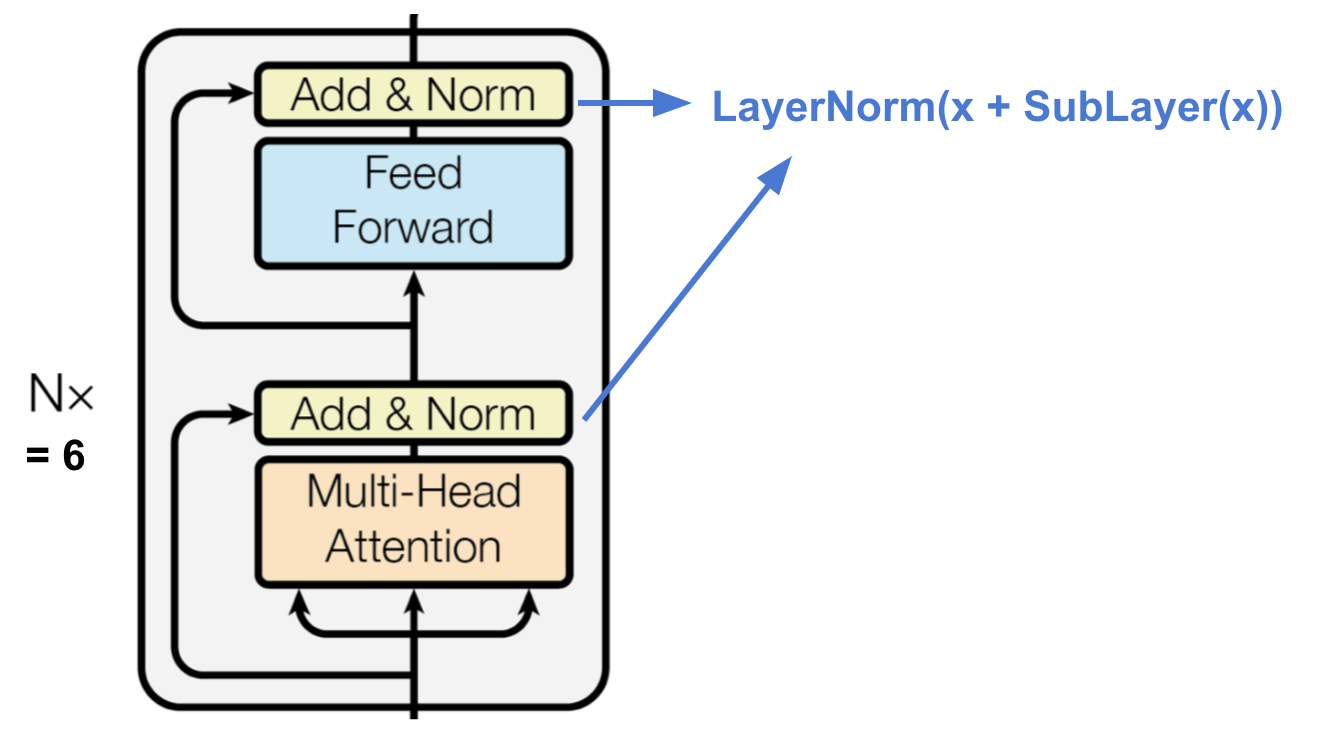
encoder产生attention-based表示
- 6个等同的层
- 每层有一个multi-head self-attention layer和一个全连接层(feed forward)
- 每个子层都采用残差链接,以及层归一化操作,输出维度均为512-dim
Decoder
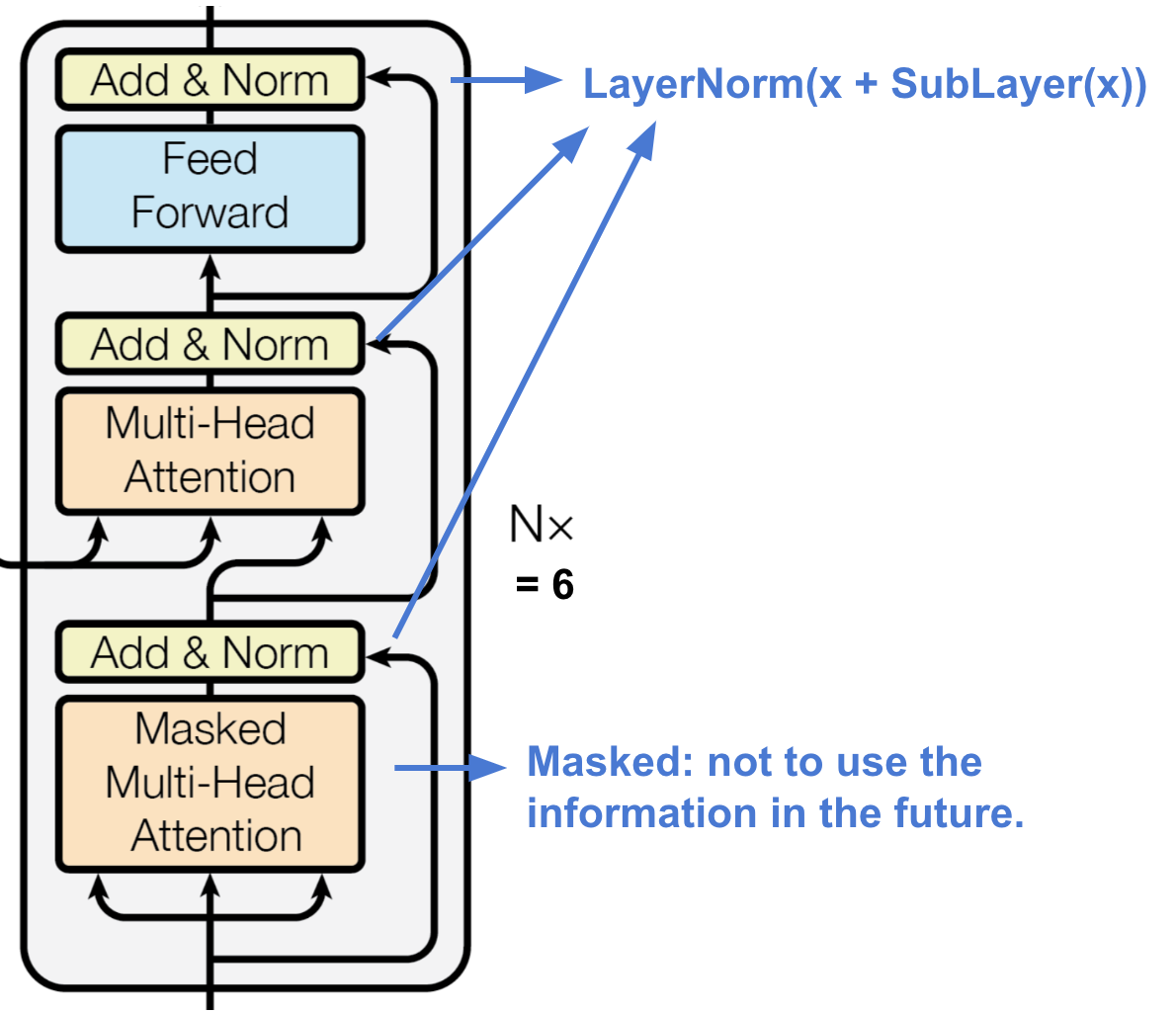
decoder通过使用context的信息,恢复或者产生想要的东西,结构描述:
-
6个等同层
-
每层两个子层,都使用multi-head self-attention layer,其中一个子层连接着一个全连接层
-
子层都有残差连接以及归一化操作
-
每层的第一个multi-head self-attention layer加了mask
The first multi-head attention sub-layer is modified to prevent positions from attending to subsequent positions, as we don’t want to look into the future of the target sequence when predicting the current position.
整个Transformer结构
Referrence
感谢下面的文章博客等,文章有些部分是中英文混合的,一个原因是怕翻译不正确,另一个原因是内容太多,偷了点懒……
https://lilianweng.github.io/lil-log/2018/06/24/attention-attention.html#summary
https://towardsdatascience.com/understanding-encoder-decoder-sequence-to-sequence-model-679e04af4346
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.3215.pdf?source=post_page—————————
https://caicai.science/2018/10/06/attention%E6%80%BB%E8%A7%88/
http://www.wildml.com/2016/01/attention-and-memory-in-deep-learning-and-nlp/?source=post_page—————————
